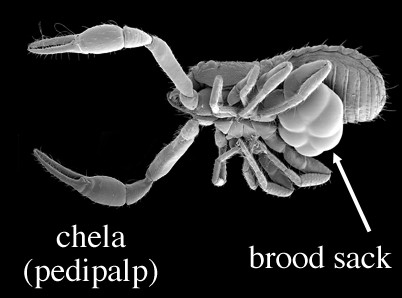
Brooding
Several different kinds of arachnids (e.g. pseudoscorpions, whipscorpions) brood their developing eggs in a sack-like structure on their venter. Mites never do this, although some oribatid mites are known to carry eggs on their backs. Spiders typically carry or guard a silken egg case. Some centipedes wrap their bodies around their developing eggs or young hatchlings.
Isopoda and Amphipoda carry their eggs in a pouch along their leg bases - the marsupium or vivarium. The pouch is formed ventrally by plate-like processes on the coxae. In cladocerans, the embryo pouch occurs under the carapace.
Spiders (Araneae) produce silk from abdominal spinnerets and often use this silk to protect their eggs. Some species carry spherical egg sacs, while others suspend them in webs or attach them to bark or leaves (as in this lynx spider).
Scorpions, some whipscorpions, and some insects carry around first stage immatures on their backs. No mites do this, although some do carry eggs, as do insects such as Belostommatidae.