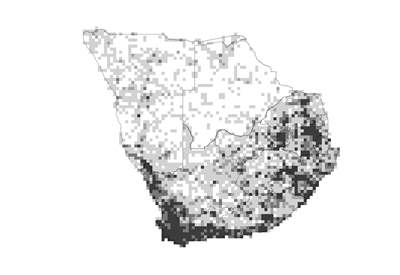
 Species distribution and density. Darker squares represent higher density of members of this family. |
Introduction
(Compositae)Daisy family
The family Asteraceae (Compositae) is one of the most familiar plant families in the world. In southern Africa it is also the largest family and is represented by 24 tribes. Of these the Senecioneae and Gnaphalieae are the largest.
Distribution
One can find members of the Asteraceae everywhere in the world, except in Antarctica. It is found throughout southern Africa with the highest concentrations in the winter-rainfall area, and in the mountainous and subtropical areas of eastern South Africa.
Number of genera in the world
ca. 1 200
Number of species in the world
ca. 21 400
Number of genera in the Flora of southern Africa region
264
Number of species in the Flora of southern Africa region
2 481
Well-known southern African genera
Berkheya, Euryops, Felicia, Helichrysum, Othonna, Senecio.
Subclasification
1. Tribe Senecioneae By far the largest tribe in the family, with 150 genera and 3 500 species in the world and 23 genera and 648 species in southern Africa. Involucre is commonly green and in one series, with or without a few much smaller outer bracts (calyculus); bracts are free or connate to various degrees; cypselae mostly cylindrical; pappus of bristles.Well-known FSA genera: Cineraria, Euryops, Kleinia, Othonna, Senecio.
2. Tribe Gnaphalieae The second largest tribe in southern Africa, with 61 genera and 586 species, worldwide with 185 genera and 1 240 species. Over 90% of the FSA species are endemic to the region. Capitula solitary or in secondary heads; involucral bracts in several rows and papery, brownish or brightly coloured, but not green; cypselae small and pappus bristles plumose or scabrid.Well-known FSA genera: Athrixia, Helichrysum, Macowania, Metalasia, Oedera, Relhania.
3. Tribe Anthemideae A fairly large tribe in the world, with 111 genera and 1 800 species. In southern Africa a sizable tribe with 35 genera and 313 species, of which many are endemic. Leaves usually glandular and aromatic; capitula discoid or radiate, mostly pedunculate, solitary or in corymbs, panicles or small compact clusters.Well-known FSA genera: Athanasia, Cotula, Eriocephalus, Osmitopsis, Pentzia, Ursinia.
4. Tribe Astereae A large tribe worldwide, with 205 genera and 3 080 species. In southern Africa the fourth largest with 23 genera and 302 species. Leaves usually alternate; capitula many-flowered; involucral bracts usually in 3-5 series, often herbaceous, usually persistent and bent downwards; cypselae laterally compressed.Well-known FSA genera: Amellus, Chrysocoma, Conyza, Felicia, Pteronia.
5. Tribe Arctotideae Most of the 25 genera and 235 species in this medium-sized tribe are endemic to southern Africa. Leaves entire, lobed or divided to the midrib, with or without small spines. Capitula usually radiate; cypselae mostly hairy; pappus of scales.Well-known FSA genera: Arctotis, Berkheya, Didelta, Gazania, Gorteria, Hirpicium.
6. Tribe Calenduleae This tribe is almost entirely endemic to southern Africa and has 12 genera and 118 species. Capitula solitary or corymbose, radiate; cypselae often winged, those of outer florets usually curved, those of Chrysanthemoides a drupe without pappus.Well-known FSA genera: Chrysanthemoides, Dimorphotheca, Osteospermum, Tripteris.
7. Tribe InuleaeThis tribe is more prolific in the world (66 genera and 687 species), than in southern Africa where 19 genera and 74 species are known. Capitula solitary; involucral bracts generally in many rows, herbaceous or cartilaginous; pappus mostly of capillary bristles.Well-known FSA genera: Calostephane, Geigeria, Pegolettia.
8. Tribe Vernonieae In southern Africa there are 15 genera and 87 species in this tribe, while there are 130 genera and 1 600 species in the world. Leaves usually alternate and the blade undivided; inflorescences cymes, corymbiform with cymose branches; capitula discoid; involucral bracts in 3-9 series; florets 1-400, mostly purple.Well-known FSA genera: Hilliardiella, Orbivestus, Polydora, Vernonia.
9. Tribe Chichorieae This tribe is represented by 14 genera and 53 species (mostly weeds) in southern Africa, but has a much larger representation (86 genera and 1 500 species) in the world. Capitula ligulate; milky latex present; florets with 5 lobes.Well-known FSA genera: *Cichorium, *Hypochaeris, *Lactuca, Sonchus, *Taraxacum.
10. Tribe Heliantheae The tribe with 113 genera and 1 500 species worldwide includes some well-known species, such as sunflowers. In southern Africa it is mostly represented by weeds and cultivated plants in 22 genera and 40 species. Herbs; leaves opposite; capitula radiate with large yellow corollas; involucral bracts in 1 or 2 rows; cypselae with a black layer in the fruit wall.Well-known FSA genera: *Helianthus, *Tithonia, *Verbesina, *Zinnia.
11. Tribe Dicomeae The tribe has 7 genera and 97 species in the world and 3 genera and 28 species in southern Africa. Capitula discoid; disc florets with relatively long lobes; involucral bracts in many series, often spiny.Well-known FSA genera: Dicoma, Macledium.
12. Tribe Mutisieae (sensu stricto)This tribe is only represented by 2 genera and 16 species in southern Africa. In the world (mainly South America and the Andes) there are 82 genera and 950 species. Style arms short-papillose; florets usually 2-lipped.Well-known FSA genera: Gerbera, Perdicium.
13. Tribe Tarchonantheae A small tribe endemic to FSA, with 2 genera and 16 species. Dioecious trees or shrubs; capitula unisexual, discoid or disciform; pappus absent or of barbed setae.Well-known FSA genera: Brachylaena, Tarchonanthus.
14. Tribe CorymbieaeThis tribe has only one genus with 14 species endemic to the Western Cape. Scapose perennial with stout rhizome; leaves linear-lanceolate, parallel-veined; capitula discoid, single-flowered, in corymb or panicle; pappus of short scales or delicate fine bristles.Well-known FSA genus: Corymbium.
15. Tribe EupatorieaeThis tribe is quite prolific in the world with 182 genera and about 2 200 species. In southern Africa it is infamous for its invasive properties and is represented by 7 genera and 13 species. Plant scandent; leaves usually opposite; cypselae with a black layer in the fruit wall.Well-known FSA genera: *Ageratum, *Campuloclinium, *Chromolaena.
16. Tribe CardueaeA tribe of 73 genera and 2 360 species in the world, but only known in southern Africa in 8 genera and 14 species, which are mostly weedy. Leaves alternate, frequently in basal rosettes; involucral bracts in many rows, usually spiny; latex present in aerial parts.Well-known FSA genera: *Carduus, *Cirsium.
17. Tribe CoreopsideaeA small tribe with only 3 well-known genera and 7 species in southern Africa, and 30 genera and 550 species in the world. Leaves commonly dissected, 1-3-pinnatifid; involucral bracts dimorphic, in 1-6 series, herbaceous, green; pappus of 2 or 3 awns, awns smooth or barbed.Well-known FSA genera: Bidens, *Coreopsis, *Cosmos.
18. Tribe HelenieaeA small tribe of 4 genera and 5 species in southern Africa, and 13 genera and 120 species in the world. Capitula radiate or discoid; involucral bracts subequal to graded; pappus of a few minute scales or absent.Well-known FSA genera: *Gaillardia, *Flaveria, Hypericophyllum, *Schkuhria.
19. Tribe AthroismeaeThe world has 6 genera and 59 species in this tribe, which is represented in southern Africa by only 1 genus and 4 species. Capitula radiate; ray florets pistillate; cypselae black or brown.Well-known FSA genus: Anisopappus.
20. Tribe Oldenburgieae This is another tribe endemic to southern Africa and has only one genus with 4 species. Leaves thick and leathery; capitula urn-shaped or almost hemispherical; ray florets 2-lipped; pappus bristles long, barbed.Well-known FSA genus: Oldenburgia.
21. Tribe Eremothamneae The 2 genera and 3 species of this tribe are endemic to southern Africa. Leaves spinose; florets yellow; style with rather long sweeping hairs.Well-known FSA genera: Eremothamnus, Hoplophyllum.
22. Tribe Platycarpheae The 2 genera and 3 species of this tribe are also endemic to southern Africa. Prostrate, stemless, clonal herbs; florets grouped in secondary heads surrounded by one or more rosettes of leaves; florets dark or light pink to white.Well-known FSA genera: Platycarpha, Platycarphella.
23. Tribe Tageteae There are 32 genera and 270 species of this tribe in the world. In southern Africa there is only 1 genus with 2 species. Commonly known as khakibos and probably one of the most common weeds. Capitula cylindric; involucral bract in 1 or 2 series; ray florets 1 or 2 per head; pappus of scales.Well-known FSA genera: *Tagetes.
24. Genus Heterolepis (unplaced in a tribe)This seemingly unrelated genus has 3 species and is endemic to southern Africa. Capitula pedunculate, radiate; involucral bracts in 2 or 3 rows; pappus of barbed bristles.Well-known FSA genus: Heterolepis.
Growth forms
Generally annual or perennial herbs, subshrubs or shrubs. There are some climbers or lianas, a number of small trees and epiphytes; very rarely aquatics.
Habitats
Found in almost all types of habitats and at all altitudes, from coastal beaches to the highest seasonally snow-capped mountains.
Flagship species
There are numerous examples of daisies that are unique to southern Africa but none of them has caught the imagination as much as Dimorphotheca sinuata (Namaqualand daisy; jakkalsblom [A]). This daisy contributes greatly to the annual flower displays in Namaqualand. It is recognised by its flattened, winged seeds and salmon or orange ray florets. Plants are annual, up to 400 mm tall and are pioneers on disturbed soils.
Significance of the family
Asteraceae species are known for a wide variety of reasons: food plants (lettuce, artichokes, sunflower); oil producers (sunflower, safflower); herbs (tarragon); ornamentals (asters, chrysanthemums, dahlias, cosmos, marigolds); insecticide (pyrethrum); medicines and herbal remedies (arnica, calendula, chamomile, tansy); and drugs (artemisien). One of the best-known South African daisies, Gerbera jamesonii (Barberton daisy), has been cultivated for many years and the breeding has led to over 900 varieties being available in worldwide trade. It is sold as pot plants but has gained popularity as cut flower and ranks 5th in the world today.
Diagnostic characters
Presence of a flowerhead (capitulum) , which consist of one or many flowers (florets) surrounded by a series of protective bracts (involucre) . Anthers usually 5, joined into a collar �. Heads can be discoid or radiate , with disc florets and/or ray florets. Ovary inferior � with 1 locule. Calyx modified into a pappus .
Did you know?
Oldenburgia grandis is one of the few indigenous Asteraceae species classified as a tree; it grows to 6 m tall and has flowerheads of 100-150 mm in diameter.