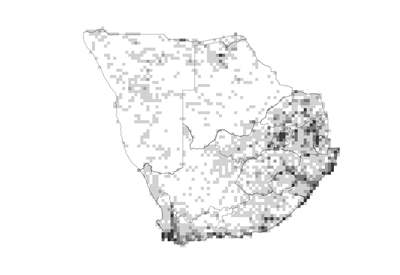
 Species distribution and density. Darker squares represent higher density of members of this family. |
Introduction
Sedge family
Many people find it difficult to distinguish between grasses and sedges, but once you know the differences, it is quite easy. Apart from the morphological differences, there are also differences in habitat requirements.
Distribution
A cosmopolitan family associated with moist situations. In southern Africa it is widespread with higher densities in the eastern parts of the country and along the coast to the Western Cape and Cederberg Range.
Number of genera in the world
109
Number of species in the world
ca. 5 500
Number of genera in the Flora of southern Africa region
37
Number of species in the Flora of southern Africa region
486
Growth forms
Grass-like herbs, usually with a perennial rhizome and often tufted.
Habitats
Primarily in moist or wet places but also in drier areas such as grassland and savanna.
Flagship species
Cyperus textilis (emezi grass, tall star sedge, basket grass; matjiesgoed [A]; umuzi [X, Z]) is quite widespread near the coasts of the Western and Eastern Cape and KwaZulu-Natal, and is often cultivated elsewhere. It grows in clumps with robust, rounded culms. Inflorescences consist of clustered spikelets subtended by a few whorls of long, flat subtending bracts. Culms are used for weaving, making sleeping mats, and were also used by the Namas to build their beehive huts (matjieshuise). It grows and spreads easily on any soil type and is ideally planted at a pond where there is enough water.
Significance of the family
Many Cyperaceae species are used traditionally to weave baskets, mats and other household items, build rafts and houses, for thatching and papermaking. They also play an important role in filtering water in wetland ecosystems and in stabilising the soil. Many species are cultivated and are attractive garden plants (e.g. Cyperus prolifer and C. papyrus). The fruits are a major source of food for birds and other animals.
Diagnostic characters
Grass-like, tufted or with rhizomes or corms. Leaves arranged in 3 ranks , crowded at the base, linear with parallel veins, consisting of blade and sheath; sheaths are closed around the stem and rarely split; culms 3-angled, rounded or flat, usually solid , with or without nodes. Inflorescence at the tip of the culm or on branches clustered at the tip , often umbellate or in heads, subtended by leaf-like bracts . Flowers small, in a single bract �. Fruit a small nut, not splitting open .
Did you know?
Carex is the largest genus in the family and has about 2 000 species in the world.