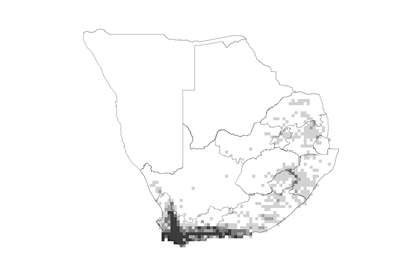
 Species distribution and density. Darker squares represent higher density of members of this family. |
Introduction
Erica family
A large family of mainly evergreen or deciduous shrubs with a cosmopolitan distribution. The plants are mostly sclerophyllous and are one of the main components of fynbos. Plants are grown for their ornamental use and as cut flowers in the flower industry.
Distribution
The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, but is found mostly in temperate, warm temperate and montane tropical areas. In southern Africa it has its highest diversity in the southern and southwestern Cape.
Number of genera in the world
ca. 140
Number of species in the world
ca. 4 500
Number of genera in the Flora of southern Africa region
2
Number of species in the Flora of southern Africa region
963
Well-known southern African genera
Erica, Vaccinium
Growth forms
Mainly evergreen or deciduous shrubs, scramblers or climbers, herbs or trees.
Habitats
Usually in seasonally dry places with a low organic component in acidic soils.
Flagship species
Erica cerinthoides (fire heath; rooihaartjie [A]; semo-monyane [SS]) is the widest distributed of all native South African ericas. In the southwestern Cape, plants can attain a height of 1.5 m. In grasslands of the Drakensberg and Mpumalanga escarpment, plants tend to be smaller in areas that are prone to fire. Flower colour varies from several shades of red and pink to white and even white with pink tips. (Photo: GN).
Significance of the family
Genera such as *Arbutus, Erica, *Kalmia and *Pieris have glossy evergreen foliage and bright flowers and are important in the cut flower industry. *Rhododendron is extremely important in horticulture. Cranberries and blueberries are among the major fruit crops produced from Ericaceae. The abundance of Erica in the Western Cape makes it important in the production of honey in this region. Honey produced from some of the *Rhododendron species can apparently be toxic.
Diagnostic characters
Leaves whorled or alternate; reduced and leathery; without bracts. Flowers regular. Corolla 4 or 5, fused into a short or obvious tube . Anthers mostly 10 (or double the number of corolla lobes), open with pores �, frequently with tails �. Ovary superior, usually with a basal disc �. Fruit a capsule, berry or drupe.
Did you know?
One of the most easily grown ericas, Erica verticillata, became extinct in the wild in the twentieth century.