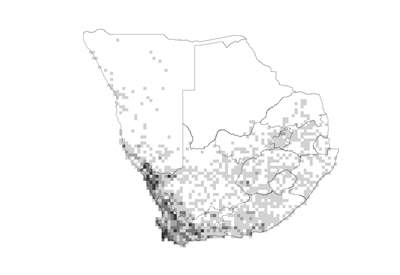
 Species distribution and density. Darker squares represent higher density of members of this family. |
Introduction
Vygie family
A large family of succulent plants with daisy-like flowers; able to survive long periods of drought. Sometimes included in the Aizoaceae but is distinguished from the latter by petals of staminodal origin, presence of needle-shaped crystals of calcium oxalate, the absence of styles and the hygrochastic fruit capsules. Two subfamilies are recognised on the basis of the placentation of the ovules (seeds).
Distribution
Most members of this family are found in southern Africa, with a few species in Australasia, Mediterranean areas, Asia, South America and North Africa. In southern Africa the highest diversity is found in the Succulent Karoo Biome.
Number of genera in the world
ca. 123
Number of species in the world
ca. 1 680
Number of genera in the Flora of southern Africa region
125
Number of species in the Flora of southern Africa region
1 761
Well-known southern African genera
Conophytum, Dorotheanthus, Mesembryanthemum, Lampranthus, Ruschia.
Subclasification
1. Subfamily MesembryanthemoideaeAxile placentation (ovules/seeds attached to the central axis of the ovary/fruit) and expanding keels reach to the centre of the fruit. Species mostly weedy, with stems and leaves soft in texture and often with prominent water cells on the leaves.Well-known FSA genera: Mesembryanthemum, Phyllobolus, Sceletium.
2. Subfamily RuschioideaeParietal or basal placentation (ovules/seeds are attached to the inside of the outer walls or the base of the ovary/fruit) and diverging expanding keels do not reach the centre of the fruit. Species are mostly dwarf shrubs with succulent leaves.Well-known FSA genera: Cleretum, Delosperma, Lampranthus, Ruschia.
Growth forms
Annual or perennial succulent herbs, shrublets or shrubs.
Habitats
Found in diverse habitats: from sand dunes to sub-alpine slopes, mostly found in winter-rainfall areas in well-drained sandy gravel, or in rock crevices.
Flagship species
Carpobrotus edulis (sour fig; suurvy [A]) is a perennial succulent forming dense mats in sandy soil. The leaves are triangular in cross-section and often reddish green. The yellow flowers fade to pink and are mostly borne during spring and early summer. The fruits are eaten fresh or dried, or are prepared as a preserve; it is also an important ingredient of oriental cooking in the Cape. The leaf juice is used medicinally to treat infections, digestive trouble and tuberculosis and is applied externally to treat eczema, wounds and burns. (Photo: RDV).
Significance of the family
Some members are cultivated as garden ornamentals (Drosanthemum, Lampranthus) or curiosity plants (Conophytum, Lithops), while others are planted to stabilise soil (Carpobrotus). Some species are used medicinally (Carpobrotus, Sceletium) to treat sore throat, fungal infections and even as stimulants. Species of Psilocaulon were traditionally used in the soap-making process and in the building of cooking shelters (kookskerms) around fires in the northwestern Cape.
Diagnostic characters
Leaves mostly opposite, succulent , without stipules. Sepals 4-6 more or less united below . Flowers regular with numerous brightly coloured, free petaloid staminodes �. Stamens numerous �. Ovary inferior � or half-inferior, usually with 5 locules. Fruit a many-seeded, hygrochastic capsule opening by means of valves ; rarely a berry or nut.
Did you know?
The capsules in this family open as a result of moisture that causes the valves to lift and the seeds are then expelled by falling raindrops.