 |
|
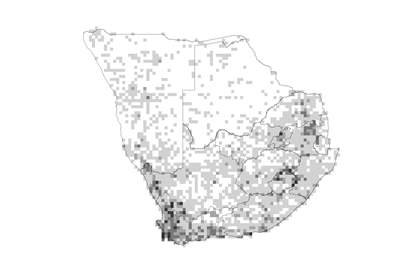 Species distribution and density. Darker squares represent higher density of members of this family. |
Introduction
(excluding Orobanchaceae)Snapdragon family
The family Scrophulariaceae (in a broad sense) consists of mainly annual or perennial herbs with flowers mostly irregular. Several genera have hairs that secrete oil to attract pollinators. There is no consensus on the circumscription of the family but ongoing molecular analyses aim to solve this problem. Genera such as Craterostigma, Mimulus, Bowkeria and Halleria have recently been assigned to other families but are retained here.
Distribution
A cosmopolitan family with higher diversity in temperate areas and tropical mountain regions. In southern Africa most species are found in the southern and western Cape extending up the West Coast through Namaqualand; also in the KwaZulu-Natal Drakensberg and on the Highveld of the northern provinces.
Number of genera in the world
ca. 269
Number of species in the world
ca. 5 100
Number of genera in the Flora of southern Africa region
66
Number of species in the Flora of southern Africa region
900
Growth forms
Mainly annual, biennial or perennial herbs, dwarf shrubs or a few shrubs and rarely trees.
Habitats
In a wide range of habitats, but common in open grassland and high mountainous areas, rarely in disturbed areas in wet tropical forest.
Flagship species
Colpias mollis (klipblom [A]) is one of a few members in the family that grows in cracks on rock faces. The species is restricted to the granite hills of Namaqualand. In springtime, plants are conspicuous on rock faces when covered with white or yellow flowers. After fertilisation, the pedicels grow away from the light towards the cracks in which the mother plant grows to deposit the ripened seed there, ensuring a suitable habitat for seedlings. This species is pollinated by oil-collecting bees.
Significance of the family
Many species are important in horticulture as ornamental plants, such as *Antirrhinum, *Calceolaria, *Linaria, Mimulus, *Pentstemon, Torenia and *Verbascum. Some medicinal plants included in the family are *Digitalis, *Leptandra, *Scrophularia and *Verbascum. The genus Diascia has co-evolved with bees of the genus Rediviva. The female bees collect oil from flowers to feed their larvae or sometimes to waterproof their nests. The length of the spurs of different Diascia species correlates with the length of the forelegs of the different bees leading to species-specific pollination.
Diagnostic characters
Leaves mostly opposite (sometimes decussate) or alternate, often opposite becoming alternate upwards, without stipules. Flowers mostly irregular ; corolla tubular , 4-5-lobed, often 2-lipped , then upper lip usually 2-lobed, lower one 3-lobed; in bud upper lobes usually external to other ones. Stamens often 4 , 2 usually longer than the other 2, rarely only 2, inserted on corolla tube . Ovary superior . Fruit mostly a 2-locular capsule , often with numerous seeds.
Did you know?
Foxglove is rich in digitalis, which was used as heart medication before artificial alternatives were available.