
Pronotum
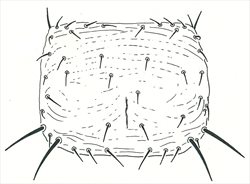
Pronotum

Antenna

Meso & metanota
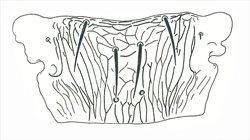
Metanotum
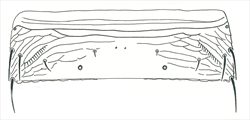
Tergite V
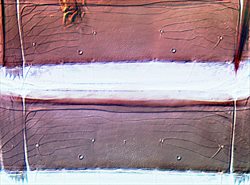
Tergites V-VI
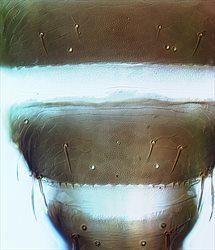
Tergites VII-IX
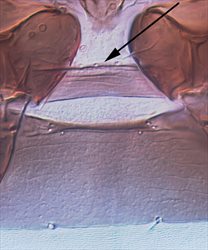
Sternites I-II

Male sternites II-VII
Both sexes fully winged. Body and legs brown; tarsi largely yellow; major setae brown, antennal segment III yellow, IV yellow with apex light brown, V–VII brown; fore wings brown with base sharply pale. Antennae 7-segmented; III–IV each with forked sense cone. Head with 2 pairs of ocellar setae; pair III shorter than distance between 2 ocelli, arising just outside ocellar triangle; postocular setae pairs I & III longer than ocellar setae III, pair II minute. Pronotum with 2 pairs of posteroangular setae; posterior margin with 3 pairs of setae; discal area without sculptured striae. Mesonotum with paired anterior campaniform sensilla; median setae arise well in front of posterior margin. Metanotum with irregular reticulation medially; median setae arising behind anterior margin; campaniform sensilla present. Fore wing first vein with 3 setae on distal half; second vein with about 12 setae. Abdominal tergite II with 3 lateral marginal setae; tergites V–VIII with paired ctenidia, on VIII posteromesad to spiracles; tergite VIII posteromarginal comb absent medially, with several stout microtrichia laterally, discal setae S1 equal in size to S2; pleurotergites with no discal setae, sculpture lines with few dentate microtrichia, posterior margin without microtrichia; tergite IX with 2 pairs of campaniform sensilla, X with median split. Sternites with no discal setae; sternite I with 2-3 very small setae near anterior margin; sternite VII marginal setae S1 arise in front of margin.
Male brown, smaller than female, antennal segment IV yellow; tergite VIII with no posteromarginal comb; tergite IX median setae slender, transverse row of 4 setae posterior to campaniform sensilla; sternal pore plates broadly transverse, but progressively smaller on III–VI.
The genus Thrips is the second largest genus in the Thysanoptera, and currently includes, worldwide, over 290 species. All members of genus Thrips lack ocellar setae I on the head, and they all have ctenidia on tergite VIII posteromesad to the spiracles. Other characters, such as number of antennal segments, number of setae on the fore wing veins, and number of discal setae on the sternites are variable between species (Palmer, 1992; Nakahara, 1994; Mound & Masumoto, 2005). Thrips viminalis is unusual amongst species of the genus Thrips in the absence of sculpture lines on the pronotal discal area.
Feeding and breeding on the young leaves of species of Salix [Salicaceae], but also recorded from Alnus [Betulaceae] and Populus [Salicaceae].
Locally common in Britain but mainly in the eastern counties of England and Scotland, and not recorded from Wales (Mound et al., 1976). Recorded widely across Europe.
THRIPIDAE - THRIPINAE
Thrips viminalis Uzel
Thrips viminalis Uzel, 1895: 196
Thrips salicaria Uzel, 1895: 182
Thrips decolor Priesner, 1927: 391
Mound LA & Masumoto M (2005) The genus Thrips (Thysanoptera, Thripidae) in Australia, New Caledonia and New Zealand. Zootaxa 1020: 1–64.
Mound LA, Morison GD, Pitkin BR & Palmer JM (1976) Thysanoptera. Handbooks for the Identification of British Insects 1 (11): 1–79.
Nakahara S (1994) The genus Thrips Linnaeus (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) of the New World. United States Department of Agriculture. Technical Bulletin 1822: 1–183.
Palmer JM (1992) Thrips (Thysanoptera) from Pakistan to the Pacific: a review. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History) Entomology Series 61 (1): 1–76.