Aplonobia
Superfamily Tetranychoidea
Family Tetranychidae
Subfamily Bryobiinae
Tribe Hystrichonychini
Genus Aplonobia
Common names: clover mites
Probability of Encounter: Medium
Quarantine importance: Medium. The genus Aplonobia has few economically important pests: most of the ~30 known species feed on native grasses, composites, and Chenopodiaceae.
-
A. histricina (Berlese) the soursob mite feeds primarily on Oxalis spp., but may damage pear.
-
A. citri is a minor pest of citrus in Australia and South Africa.
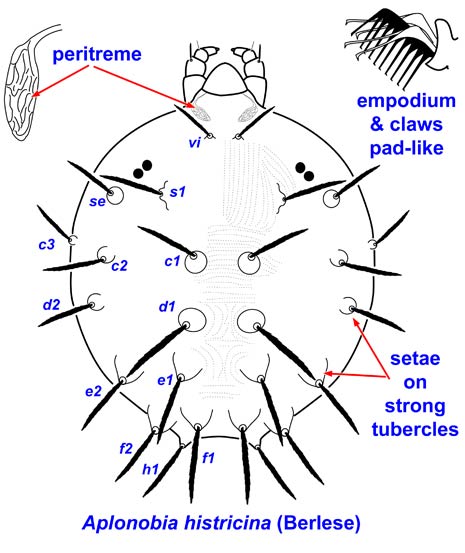
Diagnosis:
-
Claws and empodium pad-like.
-
Prodorsum with 3 pairs of setae (ve, sci, sce); without prominent lobes over gnathosoma.
-
Opisthosoma with 10 pairs of setae borne on strong tubercles (c1-3, d1-2, e1-2, f1-2, h1).
Similar taxa. The true spider mites in the Tetranychinae do not have empodia with tenent hairs. Either the claws or the empodia are hooked in other tribes of Bryobiinae. Petrobia harti (Ewing) also feeds on oxalis and has hooked empodia.
References
Baker EW & AE Pritchard. 1960. The tetranychoid mites of Africa. Hilgardia 29(11): 455-574.
Baker EW & DM Tuttle. 1994. A guide to the spider mites (Tetranychidae) of the United States. Indira Pub. House, West Bloomfield, MI: 347 pp.
Bolland HR, J Gutierre & CHW Flechtmann. 1998. World Catalogue of the Spider Mite Family (Acari: Tetranychidae). Brill: Leiden.
Helle W & MW Sabelis (eds.) 1985. Spider Mites, Their Biology, Natural Enemies, and Control, vol. 1A. Elsevier: New York.
Jeppson LR, HH Keifer & EW Baker. 1975. Mites Injurious to Economic Plants, University of California Press: Berkeley.
Mignon A & CHW Flechtmann 2004. First additions and corrections to the World Catalogue of the Spider Mite Family (Acari: Tetranychidae). Intern. J. Acarol. 30: 143-152.