Taxonomic Position
Cohort Gamasina
Subcorhort Dermanyssiae
Superfamily Phytoseioidea
Family Phytoseiidae Berlese
Subfamily Typhlodrominae Chant & McMurtry
Diagnostic characters:
-
Phytoseiid mites with 6 anterolateral setae (usually including z3, s6) and one or more of setae Z1, S2, S4 and S5.
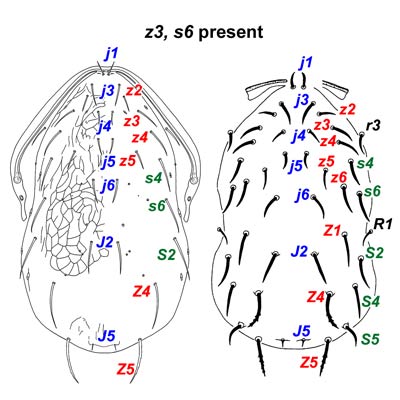
Similar
taxa. Phytoseiinae
lack setae Z1, S2, S4 and S5. Amblyseiinae
lack both setae z3 and s6. Ascids
usually have dorsal shields with 22 or more pairs of setae and only rarely (e.g. Blattisocius)
have phytoseioid corniculi.
Ecology & Distribution. Most Typhlodrominae live on vegetation and feed on mites, small insects and pollen. Some species show up in nests or flowers.
References
Chant DA. & McMurtry JA. 1994. A review of the subfamilies Phytoseiinae and Typhlodrominae (Acari: Phytoseiidae). International Journal of Acarology 20: 223-310.
Denmark, H. A. 1992. A revision of the genus Typhlodromus Scheuten (Acari : Phytoseiidae). Occasional Papers of the Florida State Collection of Arthropods 7 : 1-43.
Denmark, H. A. and Rather, A. Q. 1996. Revision of the genus Neoseiulella Muma (Acari: Phytoseiidae). International Journal of Acarology 22 : 43-77.
Schicha e.
1987. Phytoseiidae of
Australia and Neighbouring Areas. (Indira Publishing House, Oak Park, Michigan, USA.)
Schuster RO & Pritchard
EA. 1963. Phytoseiid mites of California.
Hilgardia 43: 191-285.
Tseng YH. 1976.
Systematics of the mite family Phytoseiidae from Taiwan, with a revised
key to the genera of the world (II). Journal
of the Agricultural Association of China 94: 86-128.
Walter, D.E. 1997. Notes on Australian Typhlodrominae (Acari: Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae) with descriptions of two new species of Neoseiulella Muma from tropical rainforests in Far North Queensland. Australian Journal of Entomology 36: 333-338.