Taxonomic Position
Cohort Gamasina
Subcohort Dermanyssiae
Superfamily Dermanyssoidea
Laelapidae Trägårdh s.l.
Subfamily Hypoaspidinae Vitzthum
Tribe Pseudoparasitini
Vitzthum
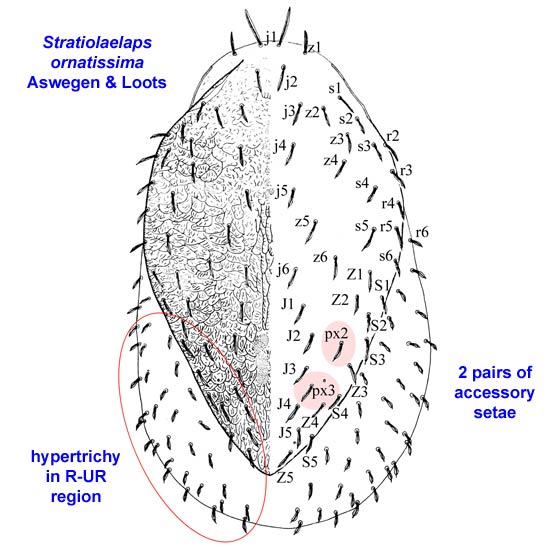
Stratiolaelaps ornatissima Aswegen & Loots
Diagnostic characters. Lamington-group species (posterior margin of sternal shield concave, gnathotectum with median and lateral processes) with tridentate fixed cheliceral digit, genital setae (st5) inserted on lateral bulges in genital shield, and extensive hypertrichy in the marginal-submarginal region.
Similar taxa.
Key to Adult females of Species of Stratiolaelaps (from Walter & Campbell 2002)
1. Fixed digit of chelicera with 2 teeth anterior to pilus dentilis, followed by serrate region; margin of gnathotectum denticulate, with longer median and lateral processes; posterior margin of sternal shield concave - lamington group (2)
- Fixed digit of chelicera with 2 teeth to either side of pilus dentilis; margin of gnathotectum denticulate, with single, smooth median process; posterior margin of sternal shield irregularly convex or produced medially - miles group (3)
2. Dorsal shield with 39 pairs of spatulate-mucronate setae, paired accessory setae px2, px3 present; postanal seta and marginal setae r6 and R1 spatulate - S. lamington
- Dorsal shield with 37 pairs of spatulate-acuminate setae, paired accessory px setae absent; postanal seta and marginal setae r6 and R1 acicular - S. womersleyi
3. Most dorsal shield setae relatively short, tips not exceeding next seta in series; setae J4 and J5 subequal, Z5 20-40% longer - 4
- Most dorsal shield setae relatively long (e.g. all podonotal setae except z1 are 51-65 µm), tips approaching or passing insertion of next seta in series; setae J4 and Z5 much longer than J5 (50-60% and 60-100% longer, respectively) - S. marilyn
4. Setae r6 similar toothers; dorsal setae of femora and genua of legs II and IV mostly spatulate; dorsal shield 585-690 µm long; fixed digit of male chelicera with one tooth posterior to pilus dentilis - 5
- Setae r6 simple; dorsal setae of femora and genua of legs II and IV simple; dorsal shield 540-590 µm long; fixed digit of male chelicera with 3-5 teeth posterior to pilus dentilis - S. lorna
5. Dorsal shield tapering gradually after level of setae S2; postanal seta short, only about 60% length of paranal setae; palp apotele with 2 subequal tines - S. miles sensu Evans and Till 1966
- Dorsal shield tapering sharply after level of setae S2; middle article of chelicera >260 µm long; postanal and paranal setae subequal in length; palp apotele with 2 subequal tines and a small basal tine - S. scimitus (Womersley)
Ecology & Distribution. Species of Stratiolaelaps are predatory and some are used in greenhouses against thrips and fungus gnats; S. ornatissima is known only from Africa.
References
Aswegen, P. I. M. and Loots, G. C. 1970. A taxonomic study of the genus Hypoaspis Canestrini sens. lat. (Acari: Laelapinae) in the Ethiopian region. Publ. cult. Co. Diam. Ang., Lisboa 82: 167-214
Berlese, A. 1892. Acari, Myriopoda et Scorpiones hucusque in Italia reperta 63, 17 text pages + Plates 1-10. (Reprint by Junk, The Hague, 1979).
Berlese, A. 1916. Centuria seconda di Acari nuovi. Redia 12, 125-177.
Chambers, R .J., Wright, E. M., and Lind, R. J. 1993. Biological control of glasshouse sciarid flies (Bradysia spp.) with the predatory mite, Hypoaspis miles, on cyclamen and poinsettia. Biocontrol Sci. Tech. 3, 285-293.
Evans, G. O., and Till, W. M. 1966. Studies on the British Dermanyssidae (Acari: Mesostigmata). Part II. Classification. Bull. Br. Mus. Nat. Hist. (Zool.) 14, 107-370.
Tenorio, J. M. 1982. Hypoaspidinae (Acari: Gamasida: Laelapidae) of the Hawaiian Islands. Pac. Insects 24, 259-274.
Wright, E.M., and Chambers, R.J.. 1994. The biology of the predatory mite Hypoaspis miles (Acari: Laelapidae), a potential biological control agent of Bradysia paupera (Dipt.: Sciardiae). Entomophaga 39, 225-235.
Womersley, H. 1956. On some new Acarina-Mesostigmata from Australia, New Zealand and New Guinea. J. Linn. Soc. (Zool.) 42, 505-599.
Zumpt, F., and Patterson, P. M. 1951. Further notes on laelaptid mites parasitic on vertebrates. A preliminary study to the Ethiopian fauna. J. Entomol. Soc. Sth Afr. 14, 63-93.
Gilyarov MS & Bregatova NG (eds) 1977.
Handbook for the Identification of Soil-inhabiting Mites, Mesostigmata. Zoological Institute of the Academy of
Sciences: Petrograd [In Russian]
Karg W.
1993. Acari (Acarina), Milben
Parasitiformes (Anactinochaeta) Cohors Gamasina Leach, Raubmilben. Die Tierwelt Deutschlands 59:
1-523. [In German]
Walter DE, Campbell
NJH. 2003. Exotic vs endemic biocontrol agents: Would the real
Stratiolaelaps miles (Berlese) (Acari: Mesostigmata: Laelapidae) please
stand up? Biological Control 26: 253-269.