Click on images to enlarge
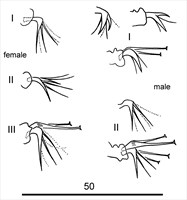
Fig. 1. Eotetranychus spinophilus - detail of female and male empodia.
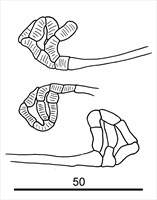
Fig. 2. Eotetranychus spinophilus, adult female - detail of anastomosing peritreme.
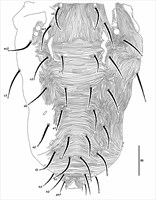
Fig. 3. Eotetranychus spinophilus, adult female.
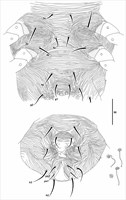
Fig. 4. Eotetranychus spinophilus, adult female, detail of venter and spermatheca.
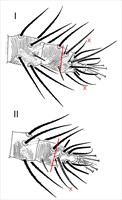
Fig. 5. Eotetranychus spinophilus - detail of female tarsi I and II (red Xs indicate overlapping setae).
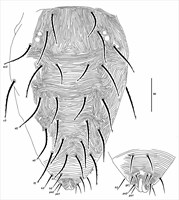
Fig. 6. Eotetranychus spinophilus, adult male.

Fig. 7. Eotetranychus spinophilus - detail of male tarsi I and II (red Xs indicate overlapping setae).
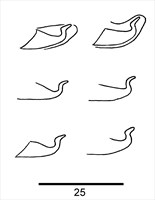
Fig. 8. Eotetranychus spinophilus, adult male - detail of aedeagus.
Material examined
types
Taxonomy
Subfamily Tetranychinae
Tribe Tetranychini
Distribution
*Australia: south eastern Queensland
Taxonomy Changes
none
Diagnosis
Female
- empodia I-IV with 3 pairs of proximoventral hairs (basal pair thicker than other pairs); no dorsal spur (Fig. 1)
- peritreme anastomosing distally (Fig. 2)
- dorsal opisthosomal striae transverse centrally, sometimes arching between setae f1-f1; lateral striae longitudinal (Fig. 3)
- dorsal setae generally as long as distance to seta in next row (central setae 31-51 long)
- pregenital striae transverse, not strongly develped (Fig. 4)
- tarsus I with sockets of one tactile setae and one solenidion proximal to, and two (ventral) tactile setae overlapping with, the socket of the proximal duplex setae (Fig. 5)
- tarsus II with the sockets of one tactile setae and one solenidion proximal to, and one (ventral) tactile overlapping with, the socket of the duplex seta (Fig. 5)
- chaetotaxy for legs I-IV:
- femora 10, 7, 2, 2
- genua 5, 5, 3, 3
- tibiae 9(1+0), 5, 5, 5
- tarsi 15(3+3), 12(2+3), 8(1+0), 8(1+0)
- body yellow to pale orange
Male as per female plus:
- empodium I with one proximoventral hair significantly thicker than other two hairs; thickened hair is uncinate (claw-like) (Fig. 1)
- empodia II-IV as in female (Fig. 1)
- peritreme as in female (Fig. 2)
- dorsal setae as in female, but slightly shorter (central setae 28-40 long) (Fig. 6)
- tarsus I with bases of 1 tactile setae and one solenidion proximal to, and two (ventral) tactile setae overlapping with, bases of proximal duplex setae (Fig. 7)
- tarsus II with bases of one tactile setae and two solenidia proximal to, and one (ventral) tactile overlapping with, bases of duplex setae (Fig. 7)
- chaetotaxy for legs I-IV:
- femora 10, 7, 2, 2
- genua 5, 5, 3, 3
- tibiae 11(3+0), 5, 5, 5
- tarsi 15(3+3), 13(3+3), 8(1+0), 8(1+0)
- aedeagus dorsally directed, with somewhat sinuous dorsal projection and no distinct knob; dorsal projection with short straight neck that bends posteriorly to form short, weakly tapering finger-like projection; dorsal projection thickened at bend producing an anterior angle; dorsal margin of shaft at 30° angle to ventral margin, abruptly bent dorsally at right angle to form dorsal projection
Hosts
*Triodia mitchelli (Poaceae)
Similar Taxa
Biology
Buck spinifex, Triodia mitchelli (Poaceae), has sharp pointed needle-like leaves that are rolled inwards, and exudes an extremely sticky resin over its leaves. Eotetranychus spinophilus lives in small populations on the surface inside the rolled leaves.
References
*Seeman, O.D., Beard, J.J., and Zhang, L. (2017) A new Australian species of Eotetranychus (Acari: Tetranychidae) from buck spinifex Triodia mitchelli (Poaceae), intraspecific variation in Eotetranychus, and the synonymy of Platytetranychus with Eotetranychus. Zootaxa 4324(3): 491-517
Notes
This species was difficult to place generically, as it has character states of both Eotetranychus and Schizotetranychus. Seeman et al. (2017) offer a discussion of the genera related to Eotetranychus.
Copyright © 2018. All rights reserved.