Taeniothrips inconsequens
Recognition data
Distinguishing features
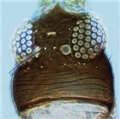
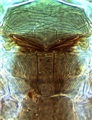
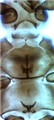
Both sexes fully winged. Body brown, with yellowish brown tarsi and antennal segment III; forewings light brown, base pale but extreme apex darker. Head longer than wide, projecting slightly in front of eyes; without sculpture between ocelli; two pairs of ocellar setae present, pair III as long as distance between compound eyes, arising between hind ocelli. Antennae 8-segmented; segments III � IV with sensorium forked. Pronotum with few discal setae, two pairs of long posteroangular setae; posterior margin with one pair of small setae laterally, also one pair of prominent setae medially arising in front of margin. Fore tarsal pulvillus with recurved claw at apex. Metanotum weakly reticulate; median setae at anterior margin; campaniform sensilla present. Forewing first vein with two to four setae on distal half; second vein with complete row of about 14 setae. Abdominal tergites with no sculpture medially; tergites VI � VIII with median setae at least half length of tergite; tergite VIII with posteromarginal comb of long regular microtrichia. Sternites without discal setae. Male smaller; sternites V � VII with small glandular area medially.
Related and similar species
The genus Taeniothrips currently includes 44 species, although 21 of these are fossils, and one is an unrecognizable fragment from Australia (Mound, 1996). Of the remaining species, one is from Africa, one from western North America, three are European in origin, and the rest are from the tropics of Asia. T. inconsequens is presumably introduced to North America, where it can usually be distinguished by the presence of a hook-like claw associated with the fore tarsal pulvillus.
Taxonomic data
Current valid name
Taeniothrips inconsequens (Uzel)
Original name and synonyms
Physopus inconsequens Uzel, 1895: 117
Euthrips pyri Daniel, 1904: 294
Physothrips calcaratus Bagnall, 1916: 221
Family placement
Thripidae, Thripinae
Common names
Pear thrips
Biological data
Life history
Breeding on young leaves before these are fully expanded (Teulon et al., 1994).
Host plants
Adults recorded from over 200 plant species, with breeding records from 34 tree species including species of Acer (Aceraceae), Fagus and Quercus (Fagaceae), Fraxinus (Oleaceae), Prunus and Pyrus (Rosaceae) (Teulon et al., 1994).
Tospoviruses vectored
None
Crop damage
Seriously damaging young leaves and causing premature leaf fall of sugar maple in north eastern USA; previously known as a pest of pear trees in California.
Distribution data
Area of origin
Europe
Distribution
Widespread across the Northern Hemisphere, from Sweden to Japan and Korea; presumably introduced to California, the northern States of the USA, and Canada.