
Female

Head & pronotum

Antenna

Meso & metanota

Pleurotergites

Abdominal tergite II
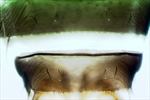
Tergites VII–VIII
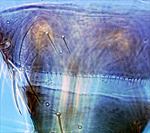
Tergite VIII

Sternites V–VII

Male sternites V–VII

Fore wing
Both sexes fully winged. Body and legs dark brown, tarsi and antennal segment III yellowish brown; fore wings brown, base paler. Antennae 8-segmented; III & IV each with a forked sense cone. Head wider than long; 2 pairs of ocellar setae; pair III small, arising just inside anterior margins of ocellar triangle; postocular setae pairs I & III slightly longer than ocellar setae III, pair II minute. Pronotum with 2 pairs of posteroangular setae, outer pair slightly shorter than inner pair; posterior margin with 3–4 pairs of setae. Metanotum reticulate medially, reticles elongate on posterior half, most reticles with faint internal markings; median setae short, arising behind anterior margin; campaniform sensilla absent. Fore wing first vein with about 7 setae on distal half; second vein with about 14 setae. Abdominal tergite II with 3 lateral marginal setae; tergites V–VIII with paired ctenidia, on VIII posteromesad to spiracles; tergite VIII posteromarginal comb of microtrichia complete but slightly irregular; pleurotergites without discal setae, but bearing ciliate microtrichia. Sternite II with 2 pairs of marginal setae, III–VII with 3 pairs; sternite II with 1–2 discal setae, III–VII with about 12 discal setae in single row.
Male smaller than female; tergite VIII with no posteromarginal comb; sternites III–VII with large transverse pore plate, discal setae arising laterally.
The genus Thrips is the second largest genus in the Thysanoptera, and currently includes, worldwide, about 295 species. Amongst these species, T. simplex is usually easily recognized as it is one of few members of the genus with short ocellar setae but with markings on the metanotum between the main lines of reticulation. All members of genus Thrips lack ocellar setae I on the head, and they all have ctenidia on tergite VIII posteromesad to the spiracles. Other characters, such as number of antennal segments, number of setae on the fore wing veins, and number of discal setae on the sternites are variable between species (Palmer, 1992; Nakahara, 1994; Mound & Masumoto, 2005).
Breeding mainly on leaves and in leaf axils, and as a result causing linear scars on the leaves and flowers of Gladiolus, Neomarica, and related Iridaceae.
Originally from southern Africa, this thrips is now worldwide wherever Gladiolus plants are grown.
THRIPIDAE - THRIPINAE
Thrips simplex (Morison)
Physothrips simplex Morison, 1930: 12
Taeniothrips gladioli Moulton & Steinweden, 1931: 20
Physothrips plurisetae Girault, 1933: 2
Taeniothrips quinani Moulton, 1936: 506.
Mound LA & Masumoto M (2005) The genus Thrips (Thysanoptera, Thripidae) in Australia, New Caledonia and New Zealand. Zootaxa 1020: 1–64.
Nakahara S (1994) The genus Thrips Linnaeus (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) of the New World. United States Department of Agriculture. Technical Bulletin 1822: 1–183.
Palmer JM (1992) Thrips (Thysanoptera) from Pakistan to the Pacific: a review. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History) Entomology Series 61 (1): 1–76.