
bituberculatus female

avius head

dicksoniae

avius antenna

dicksoniae

froggati

gomphrenae

gowdeyi

fici

howei male

driesseni

gomphrenae

ordi

timori

howei holotype
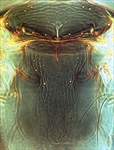
froggati metanotum

dicksoniae pelta

driesseni pelta
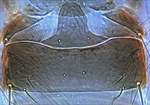
fici pelta
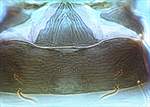
gomphrenae pelta

howei pelta

salicorniae pelta
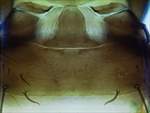
victoriensis pelta

driesseni male genitalia
Generic diagnosis
Medium sized, usually macropterous Phlaeothripinae with distinct maxillary bridge. Head usually longer than wide, vertex sometimes with transverse striae; postocular setae usually present, rarely reduced; mouth cone short; maxillary stylets deeply retracted, one fifth to one third of head width apart, with maxillary bridge. Antennae 8-segmented; segment III with 1 or 2 sense-cones, IV with 4 (rarely 2 or 3); segment VIII not constricted at base. Pronotum with little sculpture; notopleural sutures complete; usually with 5 pairs of major setae, but number and presence varies between species. Prosternal basantra present; ferna well developed; mesopresternum complete or absent medially; metathoracic sternopleural sutures absent or weakly indicated. Fore tarsal tooth usually absent in female, present or absent in male. Fore wings distinctly constricted medially; with duplicated cilia (absent in species of subgenus Trybomiella). Pelta triangular or bell-shaped; tergites II‒VII each with two pairs of sigmoid wing-retaining setae; tergite IX setae usually shorter than tube; tube shorter than head. Male tergite IX setae S2 short and stout; sternite VIII with no pore plate.
Nomenclatural data
Haplothrips Amyot & Serville, 1843: 640. Type species Phloeothrips albipennis Burmeister 1836 [= Thrips aculeatus Fabricius 1803], by monotypy
There are 238 species worldwide listed in this genus (ThripsWiki, 2022).
Australian species
Haplothrips anceps Hood, 1918: 129
Haplothrips angusi Mound & Minaei, 2007: 2946
Haplothrips avius Mound & Minaei, 2007: 2946
Haplothrips bellisi Mound & Minaei, 2007: 2947
Haplothips bituberculatus (Girault, 1927: 2)
Haplothips dicksoniae Mound & Minaei, 2007: 2950
Haplothrips driesseni Mound & Minaei, 2007: 2951
Haplothrips fici Mound & Minaei, 2007: 2952
Haplothrips froggatti Hood, 1918: 130
Haplothrips ganglbaueri Schmutz, 1913: 1034
Haplothrips (Trybomiella) gomphrenae Mound & Minaei, 2007: 2954
Haplothips gowdeyi (Franklin, 1908: 724)
Haplothrips haideeae Mound & Minaei, 2007: 2956
Haplothrips howei Mound & Minaei, 2007: 2957
Haplothips leucanthemi (Schrank, 1781: 298)
Haplothrips lyndi Mound & Minaei, 2007: 2659
Haplothrips (Trybomiella) ordi Mound & Minaei, 2007: 2960
Haplothips (Trybomiella) pallescens (Hood, 1919: 78)
Haplothrips (Trybomiella) robustus Bagnall, 1918: 209
Haplothrips (Trybomiella) salicorniae Mound & Walker, 1986: 54
Haplothrips (Trybomiella) timori Mound & Minaei, 2007: 2962
Haplothrips (Trybomiella) varius Hood, 1918: 128
Haplothrips victoriensis Bagnall, 1918: 208
Relationship data
In the Phlaeothripinae Tribe Haplothripini, there are several genera associated with Haplothrips, including Apterygothrips, Karnyothrips, Mesandrothrips, Mesothrips and Xylaplothrips.
Distribution data
Species of Haplothrips are found throughout the world. Native species of the genus are widespread across Australia, but a few species, including gowdeyi and leucanthemi are introduced to this continent from other parts of the world. Moreover, the abundant Black Plague Thrips, H. froggatti, is particularly associated with the introduced and widespread Buffel Grass (Palmer & Mound 2020). This thrips was possibly introduced to Australia along with its host plant, Cenchrus ciliaris, from some part of Africa or western Asia.
Biological data
Most of the species are flower-living, with some specific to grass florets, but some species are possibly predatory on other small arthropods.
References
Mound LA & Minaei K (2007) Australian thrips of the Haplothrips lineage (Insecta: Thysanoptera). Journal of Natural History 41: 2919–2978.
Palmer CM & Mound LA (2020) The diversity of thrips (Insecta: Thysanoptera) on buffel grass (Cenchrus ciliaris) is markedly lower than on native grasses in an urban landscape. Journal of Urban Ecology, 6 (1), 1–7. doi: 10.1093/jue/juaa024
ThripsWiki (2022) ThripsWiki - providing information on the World's thrips. Available from: http://thrips.info/wiki/ (Accessed 15.iii.2022)