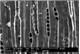
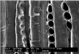
Callitris glaucophylla
Voucher: JAB185
Family: Cupressaceae Common name(s): White cypress pine, white pine, native pine
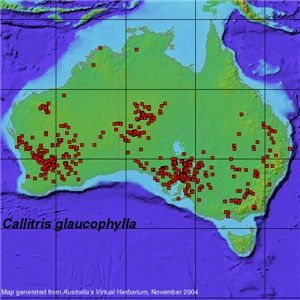
Habit: Tree to 20 m tall. Distribution: Widespread across central to southern mainland Australia.
General features: Density 800-900 kg/m3. Heartwood brown and darker than sapwood. Growth ring boundaries distinct. Wood highly resinous; resin observable to naked eye upon freshly cut specimen. Odour present (pine).
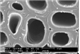
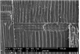
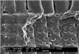
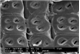
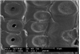
Microscopic features:
Beyond the presence or absence of vessels (which distinguishes softwoods from hardwoods) and the production of the images depicted in this factsheet, the anatomy of Callitris glaucophylla - the only softwood species treated in this research - was not examined in detail in this prototype identification tool. Further information on softwood anatomy is available in the standard list of characters for softwood identification (Richter et al. 2004).
Uses:
Aboriginal Ceremonial board; unspecified artefacts (Kamminga 2002); firewood, unspecified artefacts (Latz 1995)
European Fencing (Mitchell & Wilcox 1994); flooring, pannelling, building framework, posts, small poles (Bootle 1984: 329); telegraph poles (Maiden 1889: 545 misapplied as Frenela robusta var. microcarpa )
Notes: Cupressaceae is one of seven families belonging to the economically-important, timber-producing conifers (Pinophyta). Conifers are comprised of 65 genera and 600 species worldwide; approximately 40 of these occur in Australia (Hill 1998). Cupressaceae is comprised of 22 species within 4 genera in Australia (Hill 1998); the majority of the species belong to Callitris with C. glaucophylla being the predominant softwood species in central Australia. Coniferous families Podocarpaceae (13 species) and Auracariaceae (6 species) are also endemic to Australia whilst Pinaceae is cultivated (Hill 1998).