|
Sweetpotato
leaves, like those of most dicotyledonous plants, consist of a lamina
and a petiole with a leaf having only one
lamina or blade (simple leaf). They are spirally arranged alternately on the
stem in a pattern known as 2/5 phyllotaxis (there are 5 leaves spirally arranged
in 2 circles around the stem for any two leaves located in the same vertical
plane on the stem).
Depending
on the cultivar, the edge of the leaf lamina can be entire, toothed, or
lobed. The base of the leaf lamina generally has two lobes that can be
almost straight or rounded The shape of the general outline of the sweetpotato
leaves can be rounded, reniform (kidney-shaped), cordate
(heart-shaped), triangular, hastate, (trilobular and spear-shaped
with the two basal lobes divergent), lobed and almost divided. Lobed
leaves differ in the degree of the cut, ranging from superficial to deeply
lobed. The number of lobes generally ranges from 3 to 7 and can be easily
determined by counting the veins that go from the junction of the petiole up to
the edge of the leaf lamina. However, toothed leaves have minute lobes called
teeth which could number from 1 to more than 9. Some cultivars show
variation in leaf shape on the same plant.
The leaf
colour can be green-yellowish, green or can have purple pigmentation in part or
all the leaf blade. Some cultivars show purple young leaves and green
mature leaves. The leaf size and the degree of hairiness vary according to
the cultivar and environmental conditions. The hairs are glandular and
generally are more numerous in the lower surface of the leaf. The leaf
veins are palmated and their colour, which is very useful in differentiating
cultivars, can be green to partially or totally pigmented with anthocyanins.
The length of the
petiole ranges form very short to very long. Petioles can be green or with
purple pigmentation at the junction with the lamina and/or with the stem or
throughout the petiole. On both sides of the insertion with the lamina
there are two nectaries.
Source:
Huaman, Z. Systemic botany and morphology of the sweetpotato plant. Technical
Information Bulletin 25. International Potato Centre, Lima, Peru. 22 p.
|
Growth
habit
Root
system
Stem
Flowers
Fruit
and seeds
Storage
root
Stages
of plant development
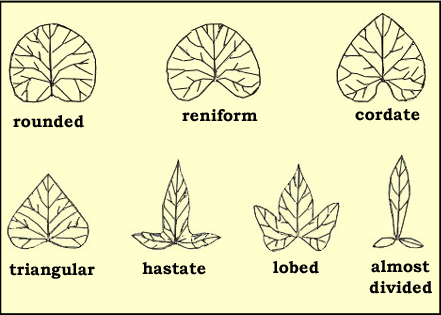
General
outline of the leaf (Z. Huaman).
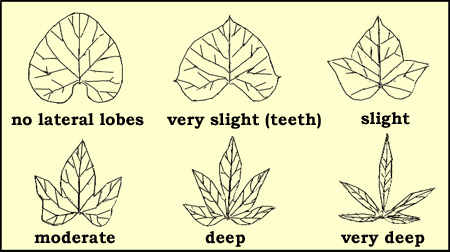
Types
of leaf lobes (Z. Huaman).
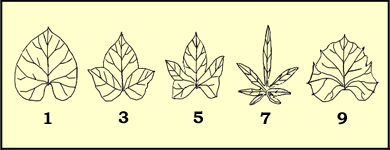
Number
of lobes (Z. Huaman).
|

