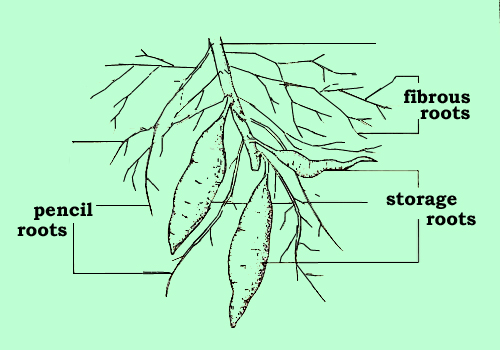
| The sweetpotato root system consists of fibrous roots - that absorb nutrients
and water and anchor the plant - and storage roots - which are lateral roots
that store photosynthetic products.
The root system of sweetpotato plants obtained by vegetative propagation
starts with adventitious roots that develop into primary fibrous roots which
branch into lateral roots. As the plant matures, thick pencil roots that
become lignified are produced. Other
roots without lignin, are fleshy and
bulky, and are called storage roots.
Plants grown from true seed form a typical root system with a central axle
with lateral branches. Later on, the central axle functions as a storage
root.
Source:
Huaman, Z. Systemic botany and morphology of the sweetpotato plant. Technical
Information Bulletin 25. International Potato Centre, Lima, Peru. 22 p.
|
Growth
habit
Stem
Leaves
Flowers
Fruit
and seeds
Storage
root
Stages
of plant development
 Parts
of the sweetpotato rootsystem (Z. Huaman). |

