
Pygidial Tuft
Locating the pygidial tuft
The pygidial tut is located at the tip of the pygidium, which is the most posterior part of the body in dorsal view.
|
Figure 1. Dorsal view of Anoplognathus. Move cursor over image to locate character |
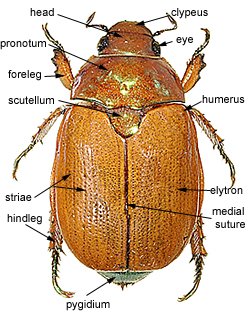
|
|
Photo Figure 1 © Kindi Smith, Australian Museum |
States of development of pygidial tuft
There are two states
-
apical tuft well-defined, by a dense group of long golden setae at tip of pygidium (Figure 2A)
-
apical tuft absent or few apical setae present, not all arising from the pygidial apex (Figure 2B)
|
Figure 2. Posterior view of apex of pygidium |
|
Move cursor over small image to view larger image |

|
scale bar equals 1mm
Photos Figure 2 © Kindi Smith, Australian Museum


