|
Parasitoids are
insects that lay eggs in or on their host then hatch and develop inside the
host's body. Hosts are usually killed as developing parasitoid consumes the
host’s organs or body fluids. Parasitoids are more host specific than insect
or spider predators. The parasitoids that attack insects are usually species of
wasps and flies.
Common
Parasitoids
Braconid wasps
(Hymenoptera: Braconidae)
|

|
Description
These are tiny
brown to blackish wasps about 2 to 15 mm in length. The abdomen is about as long
as the head and thorax combined. They have thin waist and long antennae.
Host
Several species of braconid wasps parasitise and kill a number of
different insects like aphids, caterpillars and true bugs.
|
|
parasitic wasp pupae (A. Braun).
|
|
Tachinid Flies ( Diptera: Tachinidae)
|
|
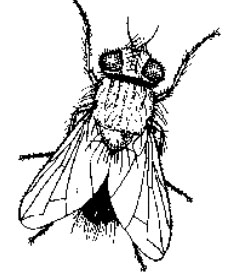
tachinid fly (CIP).
|
Description
Tachinid flies are
a very large family of active flies whose stocky bodies are covered with
bristles. They vary in size from 3 to 14 mm and resemble bees or house flies.
Live young or up to two eggs are deposited on or near a suitable host such as
larvae of moths, butterflies, sawflies, beetles, and adults of true bugs and
grasshoppers. The larvae penetrate the host and feed on its internal organs
until ready to pupate in the soil. The host almost always dies from the
parasitism. Some tachinid species are host specific , eg. some only attack leaf
rolling caterpillars while others prefer cutworms.
Hosts
The larvae are parasitic on caterpillars, beetles and grasshoppers. The adult
tachinid flies feed on nectar and secretions of aphids, scale insects and
leafhoppers while larvae are internal parasites of a variety of insects.
|
References
Shepard, B.M., G.R. Carner, A.T. Barrion, P.A.C. Ooi and H. van den Berg.
1999. Insects and their Natural Enemies Associated with Vegetables and Soybean
in Southeast Asia. Quality Printing Co. SC. USA. 108 pp.
Amalin, D.M. and E.A. Vasquez. 1993. A Handbook on Philippine Sweet Potato
Arthropod Pests and their Natural Enemies. International Potato Center, Los
Baños, Laguna, Philippines. 82 pp.
Bajwa, W. I. 2001. Insect-pathogenic bacteria. http://www.ippc.orst.edu/biocontrol/biopesticides/papers/bacteria-ent-pathogens.html
Integrated Plant Protection Center (IPPC) Oregon State University, Corvallis. 26
September, 2002.
Contributed by:
Erlinda
Vasquez and
Vilma Amante
|

