|

Black
sunken lesion on storage root of a purple-skinned cultivar (W. Martin,
APS).
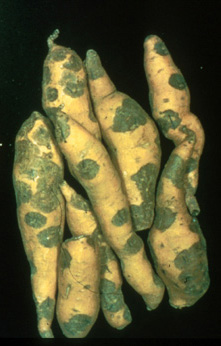
Storage
roots with black rot lesions (W.
Martin, APS).
|
Diagnostic summary
-
on storage roots, first symptoms are brown,
slightly sunken spots not more than 0.5 cm in diameter. Lesions
become firm, dry and black and can coalesce to cover the entire
root.
-
in the field plants are stunted and chlorotic
due to cankers present in underground stem. Chlorotic leaves drop.
-
in seedbeds, infected sprouts develop black
sunken necrotic lesions or cankers at the point of attachment to the
mother root. Affected shoots are girdled at soil level.
-
tissues in the rotten spots and their
surroundings have bitter taste but fruity odour.
|
Taxonomy
Economic
importance
Geographical
distribution
Symptoms
Morphology
Biology
and ecology
Host
range
Management
References
View full fact sheet |

