|
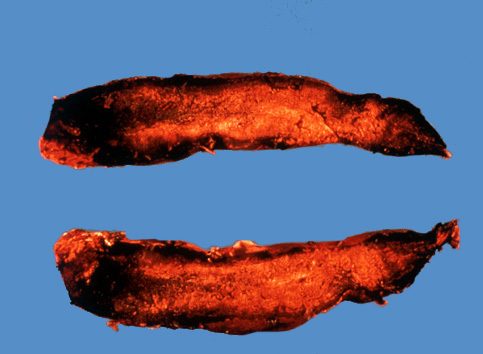
Storage
roots with charcoal rot (G. Lawrence, APS).
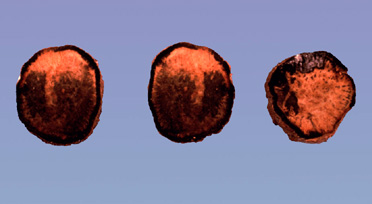
Blackening
of storage root flesh (G. Lawrence, APS). |
Diagnostic summary
- storage roots dry
up, become spongy and hard, but the periderm
remains intact over the decayed tissue.
- two zones can be
differentiated from a cross section of an infected root: the outer zone
which is black due to presence of mature sclerotia, and the inner zone
where the tissue is reddish brown and is in the process of decaying.
- stem may sometimes show
lesions at the soil line, especially during heat stress.
|
Taxonomy
Economic
importance
Geographical
distribution
Symptoms
Morphology
Biology
and ecology
Host
range
Diagnosis
Management
References
View
full fact sheet
|

