|
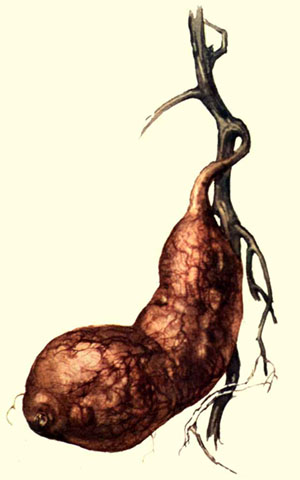
Rotten
storage root due to violet root rot (Source: Hua and Zhou, 1984). |
Diagnostic summary
- foliage becomes chlorotic
and the leaves at the base of the plant abscise prematurely.
- fibrous roots rot and are packed
together by a purplish brown mycelial mat.
- storage roots rot and covered by
bundles of packed mycelia that give a web-like appearance. Decay
develops from the distal towards the proximal (close to the plant) ends.
|
Taxonomy
Economic
importance
Geographical
distribution
Morphology
Symptoms
Biology
and ecology
Host
range
Detection
and inspection
Management
References
View full fact sheet
|

