|

Soil
rot in the root system (C. Clark, APS).
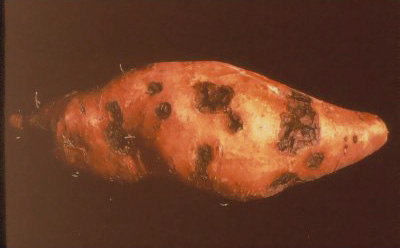
Sunken
lesions due to infection just before harvest (W. Martin, APS).
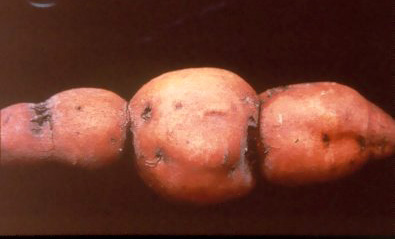
Misshapen
root due to infection at early storage root
formation (W. Martin, APS). |
Diagnostic summary
-
fibrous roots have dark lesions
and are easy to break.
-
plants become stunted, leaves are smaller and pale or bronzed and early
flowering results.
-
lesions may form on stems in contact with soil. They are
dark, dry and scaby, and occasionally the plant can be girdled.
-
lesions on storage roots ("pox") are roundish, shallow, dry, dark
spots, usually with a scaby or cracked surface.
-
when infection occurs while the root is still growing,
deformities occur as the lesion restricts expansion. The root becomes
indented or constricted at the lesion.
-
roughening of the skin rather than discrete lesions can be
observed in some genotypes.
|
Taxonomy
Economic
importance
Geographical
distribution
Symptoms
Morphology
Biology
and ecology
Host
range
Inspection
and diagnosis
Management
References
View full fact sheet
|

